29.2. Viewing Log Files
Most log files are in plain text format. You can view them with any text editor such as Vi or Emacs. Some log files are readable by all users on the system; however, root priviledges are required to read most log files.
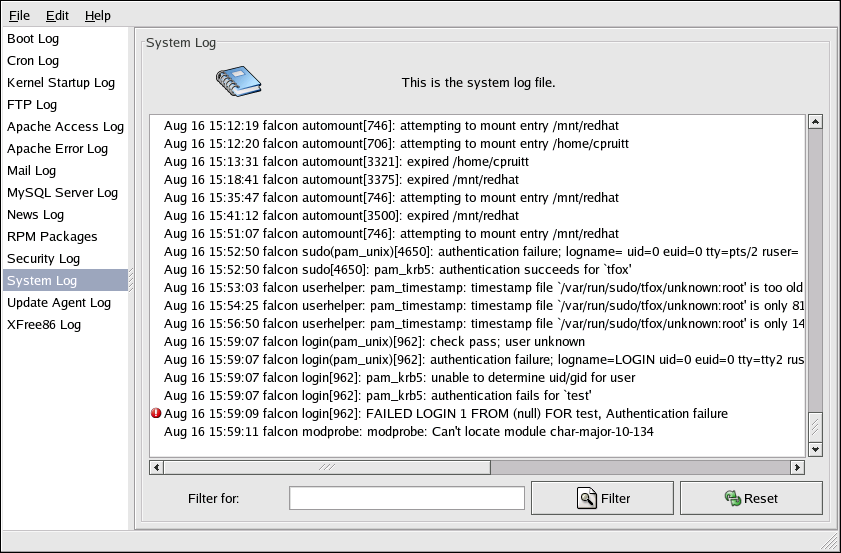
To view system log files in an interactive, real-time application, use the Log Viewer. To start the application, go to the Main Menu Button (on the Panel) => System Tools => System Logs, or type the command redhat-logviewer at a shell prompt.
The application only displays log files that exist; thus, the list might differ from the one shown in Figure 29-1. To view the complete list of log files that it can view, refer to the configuration file, /etc/sysconfig/redhat-logviewer.
By default, the currently viewable log file is refreshed every 30
seconds. To change the refresh rate, select
Edit =>
Preferences from the pulldown menu. The
window shown in Figure 29-2 will
appear. In the Log Files tab, click the up and down
arrows beside the refresh rate to change it. Click
Close to return to the main window. The refresh
rate is changed immediately. To refresh the currently viewable file
manually, select File => Refresh
Now or press
To filter the contents of the log file for keywords, type the keyword or keywords in the Filter for text field, and click Filter. Click Reset to reset the contents.
You can also change where the application looks for the log files from the Log Files tab. Select the log file from the list, and click the Change Location button. Type the new location of the log file or click the Browse button to locate the file location using a file selection dialog. Click OK to return to the preferences, and click Close to return to the main window.